A gas contained within a piston-cylinder assembly plays a crucial role in various thermodynamic processes and engineering applications. This assembly allows for the study of gas behavior under controlled conditions, providing insights into pressure, volume, temperature relationships and energy transfer mechanisms.
By exploring the fundamental principles governing gas behavior in piston-cylinder assemblies, we can gain a deeper understanding of energy conversion, heat transfer, and the operation of engines and other devices that rely on gas expansion and compression.
Thermodynamic Properties: A Gas Contained Within A Piston-cylinder Assembly
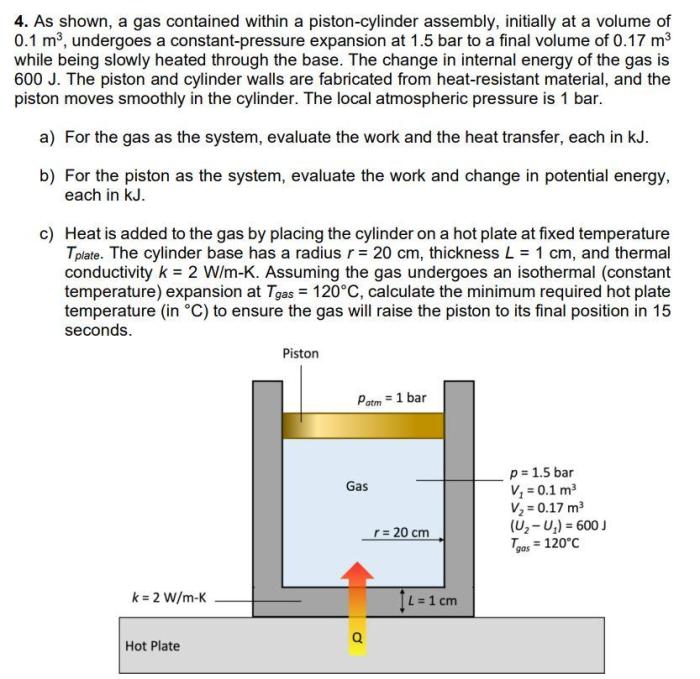
A gas contained within a piston-cylinder assembly is a system in which a gas is enclosed by a piston that can move within a cylinder. The pressure, volume, and temperature of the gas are related by the equation of state:
PV = nRT
where P is the pressure, V is the volume, n is the number of moles of gas, R is the gas constant, and T is the temperature.
Work and Heat Transfer
Work is done by the gas on the piston when the gas expands. Heat is transferred into or out of the gas when the temperature of the gas changes.
The first law of thermodynamics states that the change in the internal energy of a system is equal to the heat added to the system minus the work done by the system:
ΔU = Q
W
where ΔU is the change in internal energy, Q is the heat added to the system, and W is the work done by the system.
Applications, A gas contained within a piston-cylinder assembly
Gas contained within a piston-cylinder assembly is used in a variety of applications, including:
- Internal combustion engines
- Air compressors
- Refrigerators
- Heat pumps
In each of these applications, the gas plays a vital role in the operation of the device.
Experimental Techniques
The pressure, volume, and temperature of a gas in a piston-cylinder assembly can be measured using a variety of experimental techniques, including:
- Pressure gauges
- Volume gauges
- Thermocouples
These measurements can be used to analyze the behavior of the gas and to determine its thermodynamic properties.
FAQ Compilation
What is the equation of state for a gas in a piston-cylinder assembly?
The equation of state describes the relationship between pressure, volume, and temperature of a gas and is typically expressed as PV = nRT, where P is pressure, V is volume, n is the number of moles of gas, R is the ideal gas constant, and T is temperature.
How is work done by a gas in a piston-cylinder assembly?
Work is done by the gas when it expands, pushing the piston outward. The work done is calculated as the area under the pressure-volume curve in a P-V diagram.
What is the first law of thermodynamics in relation to a gas in a piston-cylinder assembly?
The first law of thermodynamics states that the change in internal energy of a system is equal to the heat added to the system minus the work done by the system. In a piston-cylinder assembly, this equation can be used to analyze energy transfer and conversion.


