Dna replication an overview worksheet answers – Embarking on a journey into the realm of DNA replication, this overview unveils the intricate mechanisms underlying the replication of genetic material. Delving into the steps, errors, applications, regulation, and comparisons across different organisms, this comprehensive guide illuminates the fundamental principles that govern the replication of DNA, the blueprint of life.
From the unwinding of the double helix to the precise pairing of nucleotides, DNA replication is a meticulously orchestrated process that ensures the faithful transmission of genetic information. Errors that arise during replication are swiftly detected and repaired, preserving the integrity of the genetic code.
DNA Replication Process
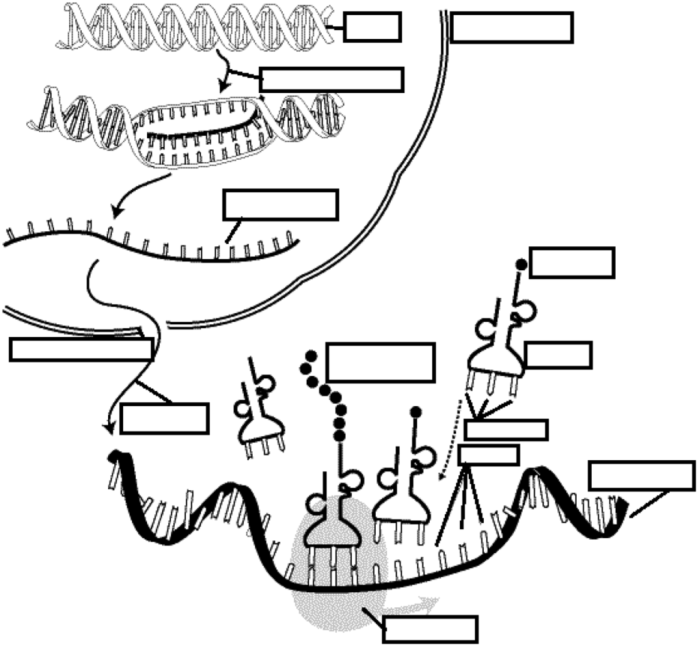
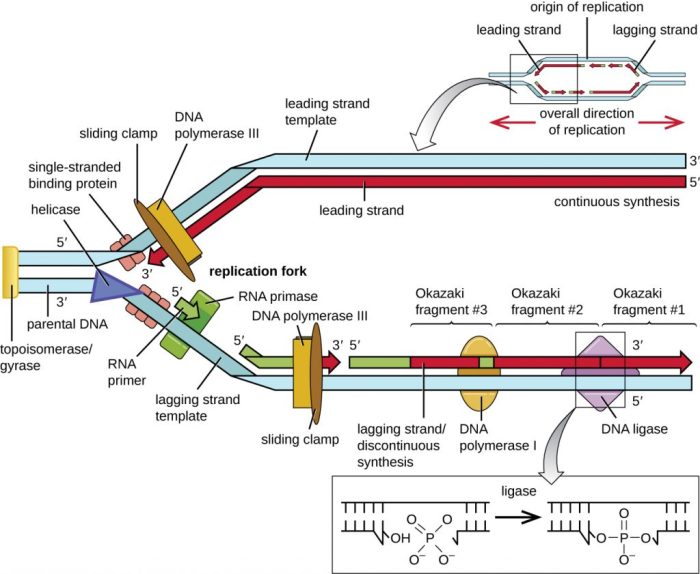
DNA replication is the process by which a cell duplicates its DNA prior to cell division. It is a fundamental biological process that ensures the accurate transmission of genetic information from one generation to the next. The process of DNA replication involves several key steps:
-
-*Unwinding
The double helix structure of DNA is unwound by enzymes called helicases, exposing the nitrogenous bases along the DNA backbone.
-*Base pairing
Free nucleotides in the nucleoplasm pair with the exposed bases on the DNA template strands according to the base-pairing rules (A with T, C with G).
-*DNA polymerase activity
DNA polymerases are enzymes that catalyze the formation of new DNA strands by adding nucleotides to the 3′ end of the growing strand, complementary to the template strand.
Errors in DNA Replication
Errors during DNA replication can lead to mutations, which are changes in the DNA sequence. Mutations can be caused by a variety of factors, including:
-
-*DNA polymerase errors
DNA polymerases can make mistakes when adding nucleotides to the growing DNA strand.
-*Environmental factors
Exposure to radiation or chemicals can damage DNA and lead to mutations.
-*Errors in DNA repair
Errors in DNA repair mechanisms can lead to the accumulation of mutations.
Applications of DNA Replication
DNA replication is a fundamental process used in various biotechnology and medical applications:
-
-*Genetic engineering
DNA replication is used to amplify specific DNA sequences through techniques like PCR (polymerase chain reaction).
-*DNA sequencing
DNA replication is used in DNA sequencing technologies to determine the sequence of nucleotides in a DNA molecule.
-*Forensic science
DNA replication is used in DNA fingerprinting to identify individuals based on their unique DNA profiles.
DNA Replication Regulation
DNA replication is tightly regulated to ensure accurate and timely duplication of DNA. Key regulatory mechanisms include:
-
-*Checkpoints
Cells have checkpoints at various stages of the replication process to monitor for errors and prevent further replication if errors are detected.
-*Control proteins
Proteins like cyclins and CDKs (cyclin-dependent kinases) control the timing and progression of DNA replication.
-*Environmental factors
Environmental factors like nutrient availability and temperature can influence the rate of DNA replication.
Comparison of DNA Replication in Different Organisms, Dna replication an overview worksheet answers
The mechanisms of DNA replication differ between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells:
-
-*Origins of replication
Prokaryotes have a single origin of replication, while eukaryotes have multiple origins of replication.
-*Replication forks
Prokaryotes have a single replication fork, while eukaryotes have multiple replication forks.
-*Termination mechanisms
Prokaryotes terminate replication at a specific termination site, while eukaryotes terminate replication when the entire DNA molecule is replicated.
User Queries: Dna Replication An Overview Worksheet Answers
What is the role of DNA polymerase in DNA replication?
DNA polymerase is the enzyme responsible for synthesizing new DNA strands during replication. It catalyzes the addition of nucleotides to the growing strand, ensuring the accurate copying of the genetic code.
How are errors in DNA replication detected and repaired?
Errors in DNA replication are detected by various mechanisms, including mismatch repair and proofreading by DNA polymerase itself. These mechanisms identify and correct errors, maintaining the fidelity of the genetic information.